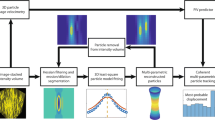
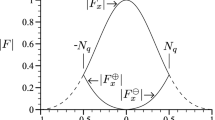
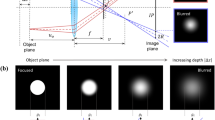
Abstract
Two techniques for multi-dimensional sizing of spherical particles are discussed and compared with one another: interferometric particle imaging (IPI) and a novel technique known as global phase Doppler (GPD). Whereas the IPI technique is known from various previous studies and uses a laser light sheet illumination of the particle field, the GPD technique is a new method and employs two intersecting laser light sheets. The resulting far-field interference pattern arises from the interference of like scattering orders from the particle, similar to the phase Doppler technique. A description of this far-field interference is given for both techniques. Both multi-dimensional particle sizing techniques sample the scattered light in the far-field by means of a defocused imaging system. The diameter of each droplet illuminated by the laser light sheet(s) is determined by measuring the angular frequency of the interference fringes in the defocused images. Combined with a pulsed laser, the technique also allows the velocity of the particle to be determined, similar to particle tracking velocimetry (PTV). However, the size of the defocused image of each particle also depends on the position of the particle perpendicular to the laser sheet, hence, with appropriate calibration, the third component of velocity is also accessible. The two techniques, IPI and GPD, are compared to one another in terms of implementation and expected accuracy. Possibilities of combining the two techniques are also discussed. Some novel approaches for the signal processing have been introduced and demonstrated with simulated and real signals.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht HE, Borys M, Damaschke N, Tropea C (2003) Laser Doppler and phase Doppler measurement techniques. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Anders K (1994) Experimentelle und theoretische Untersuchung der Tropfenverdampfung für Knudsen-Zahlen im Übergangsbereich. Shaker, Aachen, Germany
van Beeck JPAJ (1997) Rainbow phenomena: development of a laser based, non-intrusive technique for measuring droplet size temperature and velocity. PhD thesis, Technical University of Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Damaschke N, Tropea C, Stieglmeier M (1999) Planares Interferenz Partikelgrößenmeßgerät. Patent DE 199 54 702.5
Damaschke N, Senese S, Tropea C, Woite A (2000) Planare Partikelgrößenbestimmung. In: 8. Fachtagung Lasermethoden in der Strömungsmeßtechnik, paper 49. Shaker, Aachen, Germany
Damaschke N, Nobach H, Tropea C (2002) Optical limits of particle concentration for multi-dimensional particle sizing techniques in fluid mechanics. Exp Fluids 32:143–152
Glover AR, Skippon SM, Boyle RD (1995) Interferometric laser imaging for droplet sizing: a method for droplet-size measurement in sparse spray systems. Appl Opt 34:8409–8421
Hess CF (1998) Planar particle image analyzer. In: Proceedings of the 9th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, July 1998, paper 18.1
Hovenac EA, Lock JA (1992) Assessing the contribution of surface waves and complex rays to far-field Mie scattering by use of the Debye series. J Opt Soc Am A 9:781–795
Kawaguchi T, Akasaka Y, Maeda M (2002) Size measurements of droplets and bubbles by advanced interferometric laser imaging technique. Meas Sci Technol 13:308–316
Kobayashi T, Kawaguchi T, Maeda M (2002) Measurements of spray flow by an improved interferometer laser imaging droplet sizing (ILIDS) system. In: Adrian RJ, Durao DFG, Heitor MV, Maeda M, Tropea C, Whitelaw JH (eds) Laser techniques for fluid mechanics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 209–220
König G, Anders K, Frohn A (1986) A new light-scattering technique to measure the diameter of periodically generated moving droplets. J Aerosol Sci 17:157–167
Maeda M, Kawaguchi T, Hishida K (2000) Novel interferometric measurement of size and velocity distributions of spherical particles in fluid flows. Meas Sci Technol 11:L13–L18
Maeda M, Akasaka Y, Kawaguchi T (2002) Improvements of the interferometric technique for simultaneous measurement of droplet size and velocity vector field and its application to a transient spray. Exp Fluids 33:125–134
Massoli P, Calabria R (1999) Sizing of droplets in reactive fuel sprays by Mie scattering imaging. In: Proceedings of the 15th annual ILASS-Europe conference, Toulouse, France, July 1999
Min SL, Gomez A (1996) High-resolution size measurement of single spherical particles with a fast Fourier transform of the angular scattering intensity. Appl Opt 35:4919–4929
Nishino K, Kato H, Torii K (2000) Stereo imaging for simultaneous measurement of size and velocity of particles in dispersed two-phase flow. Meas Sci Technol 11:633–645
Pan XH, Luo R, Yang XY, Yang HJ (2002) Three-dimensional particle image tracking for dilute particle–liquid flows in a pipe. Meas Sci Technol 13:1206–1216
Raffel M, Willert CE, Kompenhans J (1998) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ragucci R, Cavaliere A, Massoli P (1990) Drop sizing by laser light scattering exploiting intensity angular oscillation in the Mie regime. Part Part Syst Charact 7:221–225
Schaller JK (2000) Laseroptische messtechnik: erweiterung bestehender verfahren und entwicklung neuer techniken. Habilitationsschrift, RWTH Aachen, Germany
Semidetnov N, Tropea C (2004) Conversion relationships for multidimensional particle sizing techniques. Meas Sci Technol 15:112–118
Tropea C, Xu TH, Onofri F, Grèhan G, Haugen P, Stieglmeier M (1996) Dual-mode phase-Doppler anemometer. Part Part Syst Charact 13:165–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damaschke, N., Nobach, H., Nonn, T.I. et al. Multi-dimensional particle sizing techniques. Exp Fluids 39, 336–350 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-1009-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-1009-1